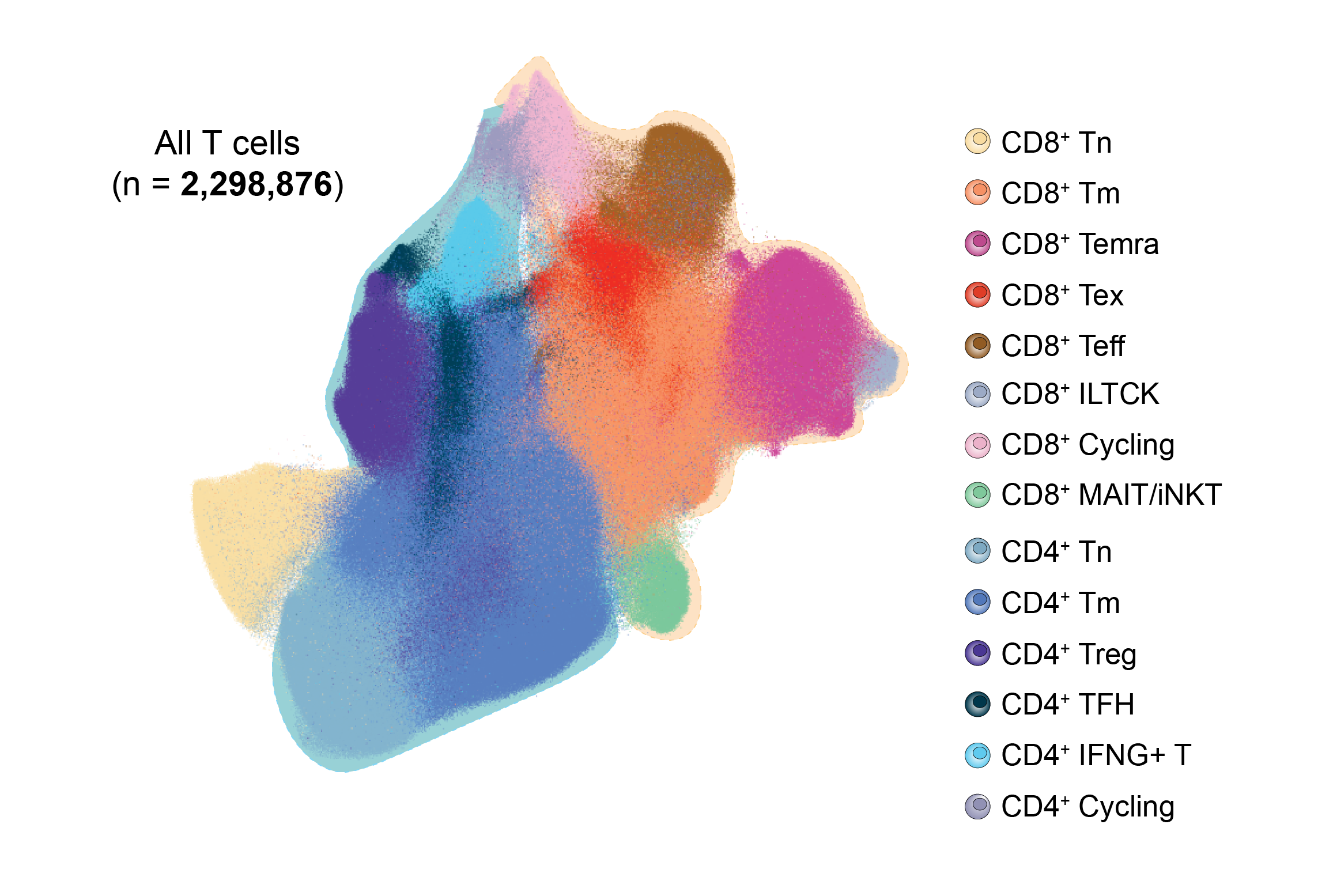Established Atlases
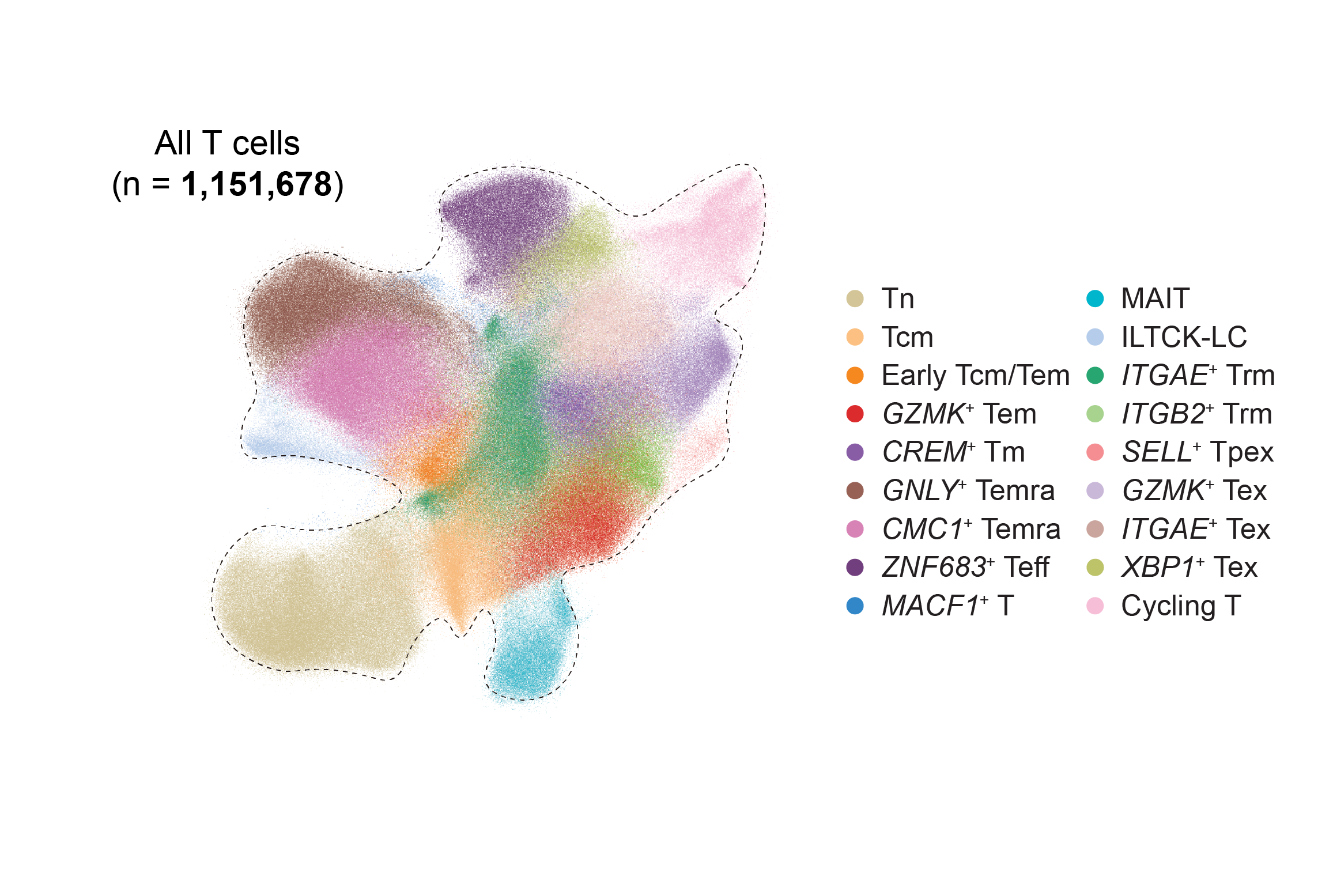
The diverse phenotype of CD8+ T cells
Link to scAtlasVAE: Github
Cite scAtlasVAE and CD8+ T cell atlas: Xue, Z., Wu, L., Tian, R. et al. Integrative mapping of human CD8+ T cells in inflammation and cancer. Nat Methods (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41592-024-02530-0